Understanding the health and wellbeing of the LGBTQ+ community is crucial for creating inclusive and supportive environments. In 2024, while there have been advancements in recognizing and addressing the unique health challenges faced by LGBTQ+ individuals, significant disparities still exist. This article explores key areas of concern, including mental health issues, access to healthcare, HIV/AIDS awareness, substance abuse and recovery support, and complications related to surgeries and therapies.
Health and Wellbeing
The health and wellbeing of LGBTQ+ individuals are influenced by various factors, including societal acceptance, legal protections, and access to inclusive healthcare. Globally, the LGBTQ+ community often faces significant health disparities compared to their heterosexual and cisgender counterparts. These disparities are rooted in stigma, discrimination, and lack of culturally competent care.
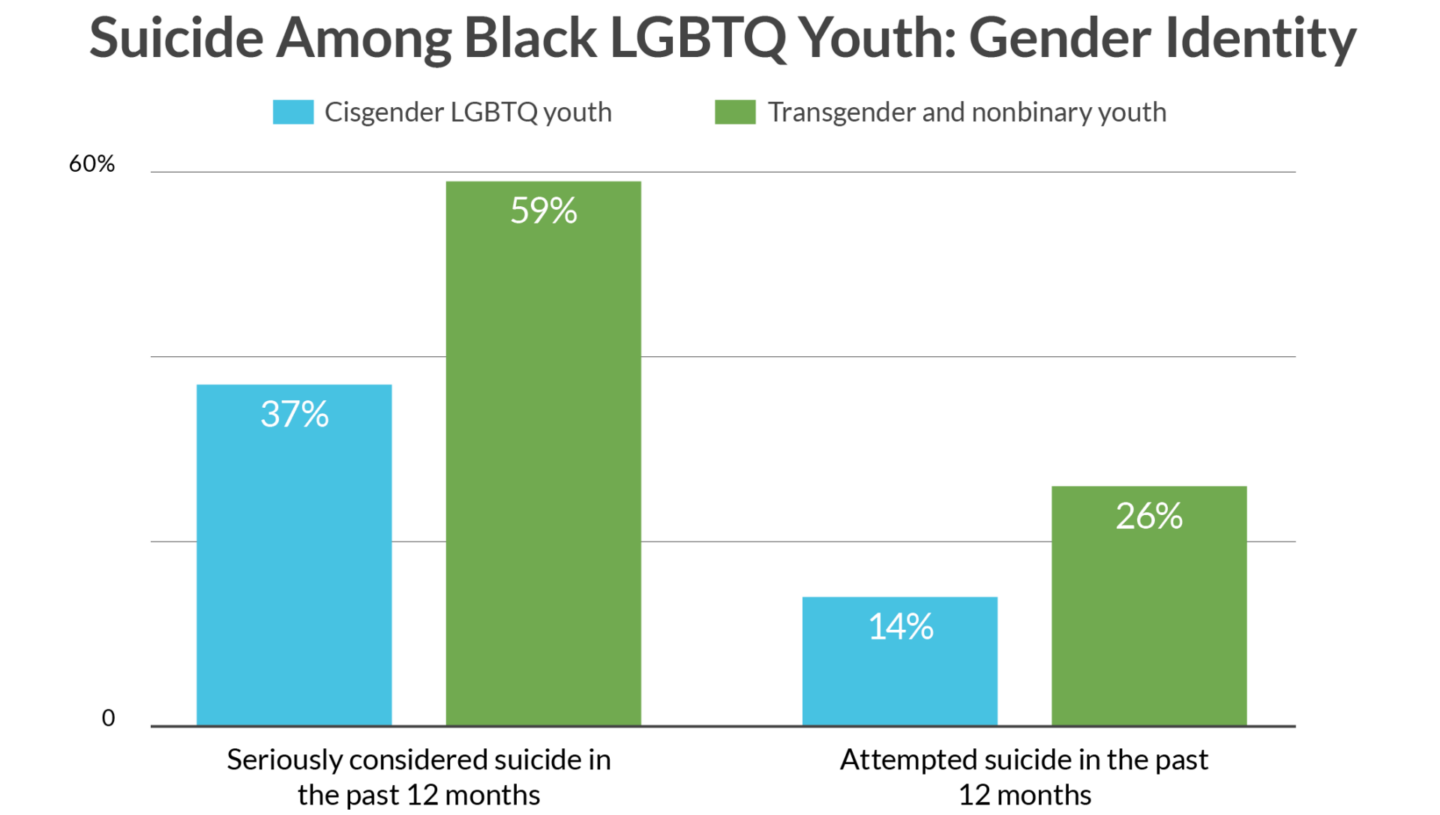
Mental Health Issues Within the LGBTQ+ Community
Mental health issues are a significant concern within the LGBTQ+ community. Studies have consistently shown that LGBTQ+ individuals are at a higher risk of experiencing mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation. This elevated risk is largely due to the stress associated with societal stigma, discrimination, and rejection.
For instance, a 2022 study published in The Lancet found that LGBTQ+ youth are more than twice as likely to experience depression and anxiety compared to their heterosexual peers. The Trevor Project’s 2023 National Survey on LGBTQ Youth Mental Health revealed that 42% of LGBTQ+ youth seriously considered attempting suicide in the past year, with rates even higher among transgender and non-binary youth.
The impact of minority stress, which refers to the chronic stress faced by members of stigmatized minority groups, cannot be overstated. This stress often stems from experiences of bullying, family rejection, and societal marginalization. Creating supportive environments, providing access to mental health resources, and promoting acceptance are essential steps in addressing these mental health disparities.
Access to Healthcare and HIV/AIDS Awareness
Access to healthcare remains a significant barrier for many LGBTQ+ individuals. Discrimination in healthcare settings, lack of provider knowledge about LGBTQ+ health issues, and financial constraints all contribute to disparities in healthcare access.
A 2021 survey by the Center for American Progress found that nearly one in five LGBTQ+ individuals avoided seeking medical care due to fear of discrimination. Transgender individuals, in particular, face challenges in accessing gender-affirming care, which is essential for their overall health and wellbeing. In many parts of the world, healthcare systems are not equipped to provide culturally competent care for LGBTQ+ patients, leading to poorer health outcomes.
HIV/AIDS continues to disproportionately affect the LGBTQ+ community, particularly gay and bisexual men and transgender women. According to UNAIDS, in 2023, 54% of new HIV infections globally were among key populations, including men who have sex with men and transgender women. Despite significant advancements in HIV treatment and prevention, stigma and discrimination hinder efforts to achieve universal access to HIV services.
Promoting HIV/AIDS awareness, increasing access to testing and prevention methods such as Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP), and addressing stigma are critical components of combating the HIV epidemic. For example, programs like India’s National AIDS Control Programme have made strides in reducing HIV transmission rates by targeting high-risk populations and increasing awareness.
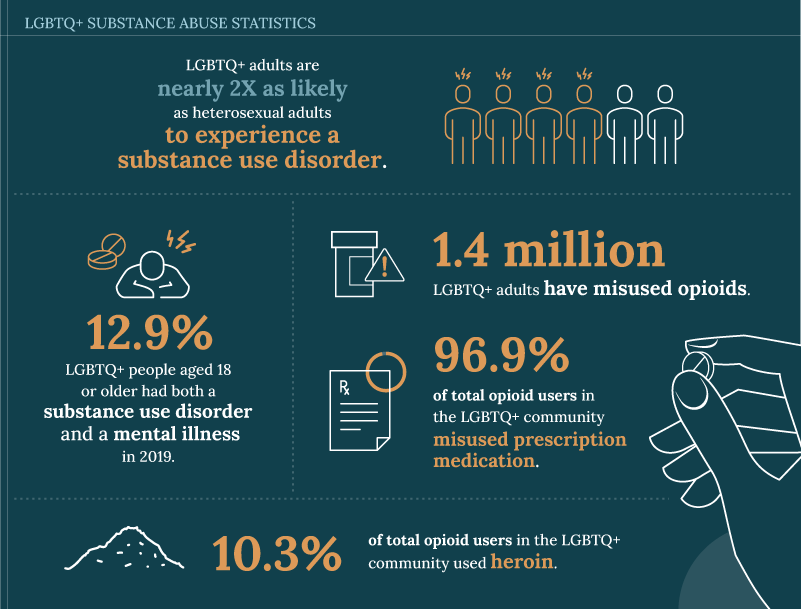
Substance Abuse and Recovery Support
Substance abuse is another critical issue within the LGBTQ+ community. Higher rates of substance use, including alcohol, tobacco, and illicit drugs, have been documented among LGBTQ+ individuals compared to the general population. This disparity is often linked to the stress of coping with stigma and discrimination, as well as the use of substances as a coping mechanism.
A 2020 report by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) indicated that LGBTQ+ adults are more likely to use substances at higher rates than their heterosexual counterparts. For example, the prevalence of substance use disorders was 15.1% among LGBTQ+ adults, compared to 7.8% among heterosexual adults.
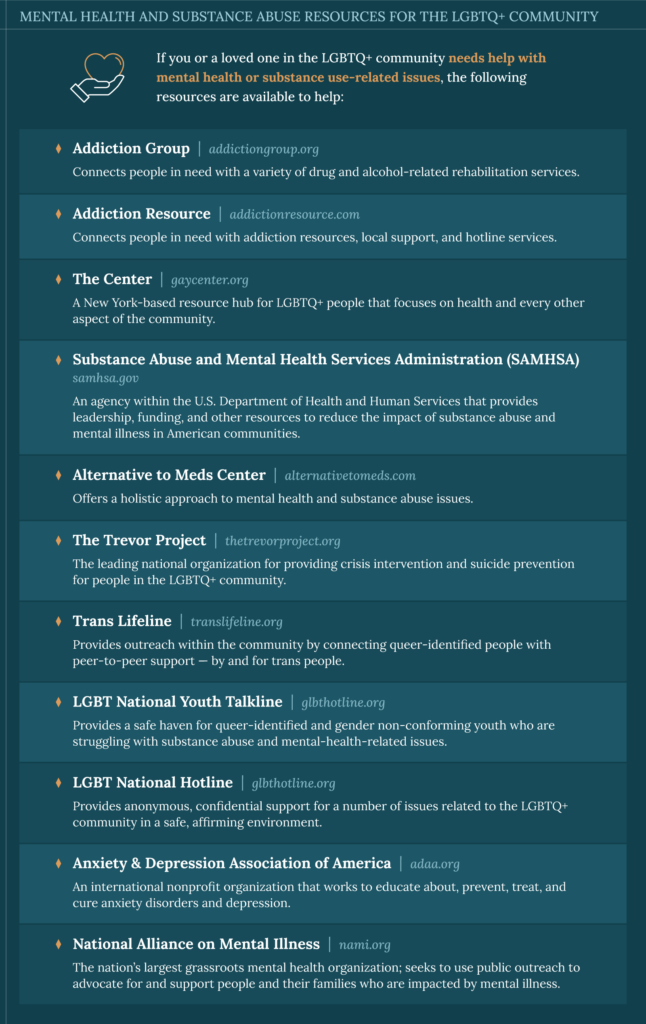
Recovery support tailored to the unique needs of LGBTQ+ individuals is crucial for addressing substance abuse within this community. Programs like the LGBTQ+ Addiction Rehabilitation Center in New York provide culturally competent care and support, acknowledging the specific challenges faced by LGBTQ+ individuals in recovery.
Complications Related to Surgeries and Therapies
For many transgender individuals, access to gender-affirming surgeries and hormone therapies is essential for their mental and physical health. However, these procedures can come with complications and challenges. Complications can arise from the surgeries themselves, such as infections, scarring, and issues with surgical outcomes.
A 2023 study published in JAMA Surgery found that approximately 30% of transgender individuals experienced some form of complication within a year of undergoing gender-affirming surgery. These complications can have significant impacts on mental health and overall wellbeing, underscoring the importance of comprehensive pre- and post-operative care.
Hormone therapy, while life-saving for many transgender individuals, can also pose health risks if not properly managed. Potential complications include cardiovascular issues, bone density changes, and metabolic concerns. Regular monitoring and access to knowledgeable healthcare providers are essential for minimizing these risks and ensuring the best outcomes.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of gender-affirming care are well-documented. According to a 2022 report by the American Medical Association, access to gender-affirming care is associated with lower rates of depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation among transgender individuals. Ensuring access to high-quality, affirming care is vital for improving the health and wellbeing of the transgender community.
Conclusion
The health and wellbeing of the LGBTQ+ community are shaped by a complex interplay of social, legal, and medical factors. While there have been significant advancements in recognizing and addressing the unique health challenges faced by LGBTQ+ individuals, disparities persist. Mental health issues, access to healthcare, HIV/AIDS awareness, substance abuse, and complications related to surgeries and therapies are all critical areas that require ongoing attention and action.
Promoting inclusive and culturally competent care, addressing stigma and discrimination, and ensuring access to necessary medical services are essential steps in improving the health and wellbeing of LGBTQ+ individuals worldwide. As we move forward in 2024, it is crucial to continue advocating for comprehensive health protections and support systems that recognize and address the unique needs of the LGBTQ+ community. By doing so, we can create a more equitable and supportive world for all.
For more stories like this, please visit here



